

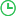
安哥拉长毛兔形态特征 安哥拉长毛兔主要价值
 发布日期:2025-12-17
来源:http://www.myxinhua.com 发布人:创始人
发布日期:2025-12-17
来源:http://www.myxinhua.com 发布人:创始人
长毛兔原译安哥拉兔,起源于小亚细亚一带,名字来自安哥拉城,即土耳其首都安卡拉。安哥拉兔从1723年由英国海员带到法国,再传到世界。后来形成了法、英、德和中四个不同的品系,长毛兔有白、黑、粟、蓝、灰、黄等多种颜色,白色兔的眼为红色,有色兔的眼睛为黑色。长毛兔白色兔毛有利染色,故饲养白色长毛免为普遍。
Angora rabbit, originally translated from Angora rabbit, originated in Asia Minor, and its name comes from Angola City, namely Ankara, the capital of Türkiye. The Angora rabbit was brought to France by British sailors in 1723 and then spread to the world. Later, four different strains were formed, namely French, English, German, and Chinese. Long haired rabbits come in various colors such as white, black, millet, blue, gray, and yellow. White rabbits have red eyes, while colored rabbits have black eyes. Long haired rabbits have white rabbit fur that is conducive to dyeing, so raising white long haired rabbits is the most common.
详细介绍 PROFILE+
Detailed Introduction to PROFILE+
常见种类
Common types
德系
German
产于德国,是目前世界上饲养普遍、产毛量的品系。我国自1978年开始引进饲养。外貌特征。全身披厚密绒毛,被毛有毛丛结构,不易缠结,有明显波浪形弯曲。面部绒毛不甚一致,有的无长毛,也有额毛、颊毛丰盛的,但大部分耳背均无长毛,仅耳尖有。耳长中等、直立,头型偏宽而短。四肢强壮,肢势端正,胸部和背部发育良好。主要优缺点。德系安哥拉兔的主要优点是产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。主要缺点是繁殖性能较低,配种比较困难,初产母兔母性较差,且适应性较差。
Produced in Germany, it is currently the most commonly raised and highest yielding strain in the world. China has been introducing animal husbandry since 1978. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with thick and dense fur, with a tuft structure that is not easily tangled and has obvious wavy bends. The facial hair is not very consistent, some without long hair, while others have abundant hair on the forehead and cheeks. However, most of the earlobes do not have long hair, only the tips of the ears. The ears are of medium length and upright, with a broad and short head shape. Strong limbs, upright posture, well-developed chest and back. Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of German Angora rabbits are high hair production, dense, slender, and soft fur, with a tuft structure, neatly arranged, and not easily tangled. The main disadvantages are low reproductive performance, difficulty in mating, poor maternal quality of primiparous female rabbits, and poor adaptability.
法系
French legal system
产于法国,选育历史较长,是目前世界上的粗毛型长毛兔。我国早在20世纪20年代就开始引进饲养,1980年以来先后引进了.些新法系安哥拉兔。外貌特征。全身披白色长毛,粗毛含量较高。额部、颊部及四肢下部均为短毛,耳宽长而较厚,耳尖无长毛或有!撮短毛,耳背密生短毛,俗称“光板”。被毛密度差,毛质较粗硬,头型稍尖。新法系安哥拉兔体型较大,体质健壮,面部稍长,耳长而薄,脚毛较少。胸部和背部发育良好,四肢强壮,肢势端正。主要优缺点,法系安哥拉兔的主要优点是产毛量较高,兔毛较粗,粗毛含量高,适于纺线和作粗纺原料。适应性较强,耐粗性较好,繁殖力较高。主要缺点是被毛密度较差,面颊及四肢下部无长毛。该免适合以拔毛方式采毛,不宜剪毛。
Produced in France with a long history of breeding, it is currently the world's famous coarse haired long haired rabbit. China began introducing animal husbandry as early as the 1920s and has introduced it since 1980 Some New French Angora rabbits. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white long hair, with a high content of coarse hair. The forehead, cheeks, and lower limbs are all short haired, the ears are wide, long, and thick, and the tips of the ears have no or no long hair! Cuff short hair, densely covered with short hair on the back of the ear, commonly known as "Guangban". Poor hair density, coarse and hard hair texture, slightly pointed head shape. The New French Angora rabbit has a larger body size, robust physique, slightly longer face, long and thin ears, and less foot hair. The chest and back are well-developed, the limbs are strong, and the body posture is upright. The main advantages and disadvantages of French Angora rabbits are high wool production, thicker rabbit hair, high content of coarse hair, and suitability for spinning threads and as raw materials for coarse spinning. Strong adaptability, good tolerance to roughness, and high reproductive capacity. The main disadvantage is that the hair density is poor, and there is no long hair on the cheeks and lower limbs. This method is suitable for plucking hair and should not be pruned.
8系
8 series
产于日本,生产性能不及德、法系安哥拉兔。我国自1979年引进饲养,分布在江浙及辽宁等省。外貌特征。全身披白色浓密长毛,粗毛含量较少,不易缠结。额部、颊部、双耳外侧及耳尖部均有长毛,额毛有明显分界线。耳长中等、直立,头型偏宽而短。四肢强壮,肢势端正,胸部和背部发育良好。主要优缺点。日系安哥拉兔的主要优点是适应性强,耐粗性好,繁殖力强,母性好,泌乳性能高。仔兔成活率高,生长发育正常。主要缺点是体型较小,产毛量较低,兔毛品质一般,且个体间差异较大。
Produced in Japan, its production performance is inferior to that of Angora rabbits from Germany and France. Since 1979, China has introduced animal husbandry and it is distributed in provinces such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Liaoning. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with thick white fur, with a low content of coarse hair, which is not easily tangled. There are long hairs on the forehead, cheeks, outer sides of both ears, and tips of the ears, with clear dividing lines on the forehead hair. The ears are of medium length and upright, with a broad and short head shape. Strong limbs, upright posture, well-developed chest and back. Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of Japanese Angora rabbits are strong adaptability, good tolerance to roughness, strong reproductive ability, good maternal function, and high lactation performance. The survival rate of young rabbits is high, and their growth and development are normal. The main disadvantages are small body size, low hair production, average quality of rabbit hair, and significant individual differences.
英系
English series
产于英国,偏向于观赏和细毛型。我国早在20世纪20~30年代就开始引进饲养。外貌特征。全身披白色、蓬松、丝状绒毛,毛质细软。头型偏圆,额毛、颊毛丰满,耳短厚,耳尖密生绒毛,形似缨穗,有的整个耳背均有长毛,飘出耳外。四肢及趾问脚毛丰盛,背毛自然分开,向两侧披下。主要优缺点。英系安哥拉兔的优点是繁殖力强,被毛白色、蓬松,可作观赏用。缺点是被毛密度差,产毛量低,体质较弱,抗病力差,且母兔泌乳力较差。
Produced in the UK, it tends to be ornamental and fine haired. China began to introduce animal husbandry as early as the 1920s and 1930s. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white, fluffy, filamentous fur, with fine and soft texture. The head shape is slightly round, with full frontal and cheek hair, short and thick ears, densely covered with fluff at the tips of the ears, resembling tassels. Some have long hair on the entire back of the ears, floating out of the ears. The limbs, toes, and feet have abundant hair, and the back hair naturally separates and falls down to both sides. Main advantages and disadvantages. The advantage of the English Angora rabbit is its strong reproductive ability, white and fluffy fur, which can be used for ornamental purposes. The disadvantages are poor hair density, low hair production, weak constitution, poor disease resistance, and poor lactation ability of female rabbits.
>丹麦系
>Danish series
原产于丹麦,1980年引入我国。外貌特征。全身披白色、蓬松、柔软绒毛,头呈圆形或稍长型,皮肤紧密、细致,被毛丰满、浓密,多为短毛。有的耳尖长有!撮长毛,俗称“1撮毛”。主要优缺点。丹麦系安哥拉兔的主要优点是绒毛不易结块,产毛量较高主要特点是繁殖性能较差,与德系安哥拉兔繁殖性能相似。
Originating from Denmark, it was introduced to China in 1980. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white, fluffy, and soft fur, the head is round or slightly long, the skin is tight and delicate, and the coat is full and dense, mostly short hair. Some ears have long tips! Cuo Mao, commonly known as "1 Cuo Mao". Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of Danish Angora rabbits are that their fur is not easily clumped and their hair production is high. Their main feature is poor reproductive performance, which is similar to that of German Angora rabbits.
中系
Chinese-style
主要饲养于上海、江苏、浙江等地,系引进法系和英系安哥拉兔互相杂交,并导人白兔血液,经长期选育而成,1959年正式通过鉴走,命名为中系安哥拉兔。
Mainly raised in Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and other places, the Angora rabbit is introduced from the French and English lineages and crossbred with each other, and introduced into the blood of Chinese white rabbits. After long-term breeding, it was officially named the Chinese Angora rabbit in 1959.
外貌特征。中系兔的主要特征是全耳毛,狮子头,老虎爪。耳长中等,整个耳背和耳尖均密生细长绒毛,飘出耳外,俗称“全耳毛”。头宽而短,额毛、颊毛异常丰盛,从侧面看,往往看不到眼睛,从正面看,也只是绒球团。脚毛丰盛,趾间及脚底均密生绒毛。骨骼细致,皮肤稍厚,体型清秀。
Appearance features. The main characteristics of Chinese rabbits are full ear hair, lion head, and tiger claws. The ear length is medium, and the entire back and tip of the ear are densely covered with slender hairs that float out of the ear, commonly known as "whole ear hair". The head is wide and short, with exceptionally abundant hair on the forehead and cheeks. When viewed from the side, the eyes are often not visible, and when viewed from the front, they are only fluffy balls. The foot hair is abundant, with dense fuzz between the toes and on the soles of the feet. The bones are delicate, the skin is slightly thick, and the body shape is delicate.
主要优缺点,中系兔的主要优点是性成熟早,繁殖力强,母性好,仔兔成活率高适应性强,较耐粗饲。体毛洁白,细长柔软形似雪球,可兼作观赏用。主要缺点是体型小,生长慢。产毛量低,被毛纤细,结块率较高,一般可达15%左右,公兔尤高。
The main advantages and disadvantages of Chinese rabbits are early sexual maturity, strong reproductive ability, good maternal function, high survival rate of offspring, strong adaptability, and tolerance to coarse feeding. The body hair is pure white, slender and soft, resembling a snowball, and can also be used for ornamental purposes. The main disadvantages are small body size and slow growth. Low hair production, fine coat, high clumping rate, generally up to 15%, especially for male rabbits.
形态及特征
Form and characteristics
毛发很浓密且是竖起的,但却不会像其它安哥拉免般常常掉毛,而质地亦较为坚韧。德系兔属细毛型,被毛密度大,每平方厘米达16000-18000根。有毛丛结构,不易缠结,产毛量高,年产毛量公兔为1190克,母兔为1406克,者达1700-2000克,毛长5.5-5.9厘米,年整殖3-4胎,每胎产仔6-7只,配种受胎率为53 6%本地安哥拉兔是我国在英系、法系安哥拉兔杂交的基础上掺入我国本地兔的血统并经长期选育而形成,其脚如虎爪,脚毛丰盛,背毛腹毛齐全。本地安哥拉免体型较小,骨骼较细,成年体重2.5~3.0千克。成年雄性兔体重达4.5千克,雌兔达4.9千克。公兔年产毛量为1千克以上,母兔1.2千克以上,毛质量好,不易结块,特一级毛的比例占总产毛量的75%以上。母兔初配年龄200日龄,年产4.5窝,胎产活仔7.2只。
The hair is thick and erect, but it does not shed hair as frequently as other Angolans, and the texture is also relatively tough. German rabbits belong to the fine haired type, with a high hair density of 16000-18000 hairs per square centimeter. The Angora rabbit has a tuft structure, is not easily tangled, and has a high hair production. The annual hair production of male rabbits is 1190 grams, and that of female rabbits is 1406 grams, with the highest reaching 1700-2000 grams. The hair length is 5.5-5.9 centimeters, and there are 3-4 litters per year, with 6-7 offspring per litter. The breeding and conception rate is 53.6%. The Angora rabbit is a hybrid of English and French Angora rabbits in China, with the addition of local rabbit bloodlines and long-term breeding. Its feet are like tiger claws, with abundant foot hair and complete dorsal and ventral hair. Local Angolans have a smaller body size and thinner bones, with an adult weight of 2.5-3.0 kilograms. Adult male rabbits weigh 4.5 kilograms, while female rabbits weigh up to 4.9 kilograms. The annual hair production of male rabbits is over 1 kilogram, and that of female rabbits is over 1.2 kilograms. The hair quality is good and not easy to clump. The proportion of special grade hair accounts for more than 75% of the total hair production. The first mating age of the female rabbit is 200 days old, with an annual production of 4.5 litters and 7.2 live offspring.
我孥锋的推届演1銫?讴巔弥郑年底餓始稭觴灶引进德系安哥拉兔,刚引进时,对我国的环境适应性较差,抗病力差,体型外貌不一致,遗传性不稳定,对饲养管理条件要求高。经过多年的适应和培育,该兔的成年兔体重平均4.23千克,比原种提高10.92%,平均年产毛量781克左右,一次剪毛量比原种提高11.27%。
I, Ying Feng, introduced the German Angora rabbit to our country at the end of the year. When it was first introduced, it had poor adaptability to the environment, poor disease resistance, inconsistent body shape and appearance, genetic instability, and high requirements for feeding and management conditions. After years of adaptation and cultivation, the average weight of adult rabbits in this rabbit is 4.23 kilograms, which is 10.92% higher than the original breed. The average annual hair production is about 781 grams, and the amount of hair cut per time is 11.27% higher than the original breed.
饲养方法
Feeding method
三观察
Three observations
一观察兔的精神状态,如发现免精神不振,眼睛无神,眼角湿润,耳色过红或过青,背毛蓬乱,卧伏不起或打喷,呼吸急促,这是兔不健康的表现。二观察兔的食欲情况,不健康免食欲不振,吃得少或蹲在一旁拒食。三观察兔粪形状的变化。患肠胃病的兔,粪便一头尖;患便秘的兔,粪干硬,大小不一致。
When observing the mental state of a rabbit, if it is found to be lacking in energy, with lifeless eyes, moist corners of the eyes, ears that are too red or too green, messy back hair, inability to get up or spray, and rapid breathing, these are unhealthy manifestations of the rabbit. Observe the appetite of the rabbit, and if it is unhealthy, it may lead to loss of appetite, eating less or squatting on the side to refuse to eat. Observe the changes in the shape of rabbit feces. Rabbits suffering from gastrointestinal diseases have a pointed head of feces; Rabbits suffering from constipation have dry and hard feces of varying sizes.
五不喂
Five not feeding
是不喂露水草;二是不喂腐烂发霉的饲料;三是不喂带泥、带沙土的饲料;四是不喂异味的草;五是有些饲料在某些生长阶段
Not feeding dew water plants; Secondly, do not feed on rotten or moldy feed; Thirdly, do not feed feed with mud or sand; The fourth is not to feed with smelly grass; Number five, some feed is available at certain growth stages
不能喂,如荞麦开花时,亚麻在籽粒、冠茎成熟时有毒,土豆特别是未成熟的土豆不能喂。
Cannot be fed, such as when buckwheat blooms, flax is toxic when the seeds and stems mature, and potatoes, especially immature potatoes, cannot be fed.
》九注意
》Nine Attention
一要注意预防疾病。二要注意选好种兔。三要注意适时选配。四要注意种兔管理,公母免都不能喂得过肥过瘦。公兔在配种期料量应增加25%,适当喂些豆类及大麦芽等:适时增加母兔营养,催情保胎,避免死胎。五要注意仔兔管理。应搞好母兔的产仔哺乳、饲喂、断乳及分群管理(大小兔分开饲养,每放15只为宜)。六要注意饲料多样化。七要注意给有特殊情况的兔"吃偏饭"。在饲喂中对老、弱、病、残、孕兔、哺乳母兔、仔幼免都要适当照顾,每天喂食4-5次;对病免要单独饲养和,防止传染。八要注意笼舍的方向和大小。夏朝东,冬朝南,兔笼长度大于兔体长的3倍,高出免体1.5倍。九要注意防止兔受三怕:一怕惊吓,二怕潮湿,三怕曝晒。
One must pay attention to preventing diseases. Secondly, it is important to choose the right breed of rabbits. Pay attention to timely selection and matching. Attention should be paid to rabbit breeding management, and both males and females should not be fed too fat or too thin. During the mating period, male rabbits should increase their feed intake by 25% and be fed with appropriate amounts of beans and barley malt. Female rabbits should also be given timely nutrition to promote estrus and prevent stillbirth. Pay attention to the management of young rabbits. We should do a good job in the birth, feeding, weaning, and grouping management of female rabbits (separate feeding of large and small rabbits, with 15 rabbits per square meter). Pay attention to the diversification of feed. Pay attention to providing special meals for rabbits with special circumstances. During feeding, appropriate care should be taken for the elderly, weak, sick, disabled, pregnant rabbits, nursing mothers, and young rabbits, feeding them 4-5 times a day; Disease control should be raised and treated separately to prevent transmission. Pay attention to the direction and size of the cage. Summer faces east, winter faces south, and the length of the rabbit cage is greater than three times the length of the rabbit's body and 1.5 times higher than the free body. Nine precautions should be taken to prevent rabbits from being afraid of three things: first, being scared, second, being damp, and third, being exposed to sunlight.
科学采毛
Scientific hair harvesting
选择合适的采毛时间和采毛方法,不仅能提高兔毛的产量和质量,还有利于种兔的配种繁殖。另外,适当缩短长毛免采毛的间隔时间,还可以增加长毛兔的年产毛量。长毛兔的采毛方法主要有剪毛和拔毛2种,拔毛又分为拔光和拔长留短2类。不同种类的长毛兔,采用的拔毛方法也不一样,粗毛型兔宜采用手拔毛,绒毛型兔则以剪毛为好。采用剪毛方式来毛,速度快、省时间,对幼兔、母兔没有不良影响,采用拔长留短则可以提高优级毛数量,而采用拔光的方法既可以提高粗毛质量,还可以提高产毛总产量。
Choosing the appropriate hair harvesting time and method can not only improve the yield and quality of rabbit hair, but also facilitate the breeding and reproduction of breeding rabbits. In addition, appropriately shortening the interval between long haired rabbits without hair harvesting can also increase the annual hair production of long haired rabbits. There are two main methods for harvesting the fur of long haired rabbits: shearing and plucking, which can be further divided into two categories: plucking the fur completely and plucking the long and leaving the short. Different types of long haired rabbits use different methods of plucking their fur. Coarse haired rabbits should be plucked by hand, while hairy rabbits should be pruned. Using shearing method for hair production is fast, time-saving, and has no adverse effects on young and female rabbits. Pulling out the long and leaving the short can increase the quantity of high-quality hair, while using the method of pulling out the light can not only improve the quality of coarse hair, but also increase the total yield of hair production.
采毛时,一般从背部中线开始,由后向前推剪,依次为体侧、臀部、颈部、颌下、头部、腹部和四肢,也可以按照习惯进行。需要提醒的是,不能伤到长毛兔的皮肤,尤其是母兔的乳头,防止粗暴拔毛,万一失手伤到皮肤,应立即搽碘酒、止血。剪毛要一刀剪断,不剪二茬毛,以免降低兔毛等级。采毛时要边采毛边分级,将兔毛按级存放和保管。季节不同,采毛方法也不相同,夏季剪毛方式,剪毛尽量选择早、晚凉爽时进行,冬季采用拔毛方式,对于妊娠的母兔,还应留下腹毛。另外,采毛的器械还要注意,病兔剪毛必须单独进行,以防止皮肤病及其他传染病传播。
When collecting hair, it is generally started from the midline of the back, pushed and cut from back to front, in order of the body side, buttocks, neck, submandibular area, head, abdomen, and limbs. It can also be done according to habits. It should be noted that the skin of long haired rabbits, especially the nipples of female rabbits, should not be injured to prevent rough plucking. In case of accidental skin injury, iodine solution should be immediately applied for disinfection and hemostasis. To cut the rabbit hair, one should cut it with one knife, not two strands, in order to avoid lowering the grade of the rabbit hair. When collecting fur, it is necessary to classify the raw edges and store and preserve the rabbit fur according to the grade. The methods of harvesting fur vary depending on the season. In summer, it is best to prune the fur, preferably in the cool early or late hours. In winter, it is best to pluck the fur. For pregnant female rabbits, abdominal fur should also be left behind. In addition, the equipment used for hair collection should also be disinfected, and the shearing of diseased rabbits must be done separately to prevent the spread of skin diseases and other infectious diseases.
四、病害防治
4、 Disease prevention and control
1、坚持自繁自养,新购兔隔离观察为了防止传染病的侵入,是自繁自养,确需引种时,要从非疫区购买。购入后隔离饲养2周以上,确认无病后方可放入兔场饲养。
1. Adhere to self breeding and self raising, and isolate newly purchased rabbits for observation. In order to prevent the invasion of infectious diseases, it is best to self breed and self raise. If introduction is necessary, it should be purchased from non epidemic areas. After purchase, isolate and raise for more than 2 weeks, and confirm that there is no disease before putting it into the rabbit farm for breeding.
2、搞好卫生卫生是防病的重要一环,通过以减少和消灭环境中的病原体,切断传播途径。饲养人员要求在更衣、换鞋、洗手后进入兔舍,进入场区的大门口应设池。外来工具、物品要经后再使用,常用工具及时清洗和晒。免舍、兔笼要坚持每天清扫一次,每周带免一次。
2. Good hygiene and disinfection is an important part of disease prevention. Through disinfection, pathogens in the environment can be reduced and eliminated, and transmission routes can be cut off. Breeding personnel are required to enter the rabbit house after changing clothes, shoes, and washing hands, and a disinfection pool should be set up at the entrance of the field. Foreign tools and items should be disinfected before use, and commonly used tools should be cleaned, disinfected, and sun dried in a timely manner. Free sheds and rabbit cages should be cleaned once a day and disinfected once a week.
3、搞好免疫免疫是控制传染病发生的一种重要手段,免疫搞好了,疫病就能得到有效的控制。由于各地区、各免场的疫病流行情况不同,因此也就不可能有一个可供各地统一使用的免疫程序,这就需要各养免场在实践中总结经验,制定符合具体情况的免疫程序。下面是几种常见病的免疫方法:
3. Improving immunity is an important means of controlling the occurrence of infectious diseases. Once immunity is improved, the disease can be effectively controlled. Due to the different epidemic situations in various regions and immunization sites, it is impossible to have a unified immunization program that can be used in different areas. This requires each immunization site to summarize their experience in practice and develop the best immunization program that is suitable for specific situations. Here are several common immunization methods for diseases:
兔瘟。仔兔40~45日龄皮下注射兔瘟蜂胶疫苗1笔升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,在60日龄时再加强免疫接种一次,以后每6个月免疫注射一次。若本病发生流行,在流行地区需加倍剂量免接种。兔巴氏杆菌病。仔兔断奶后每只注射兔离巴氏杆菌苗1毫升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。魏氏梭菌病。断奶仔兔皮下注射魏氏梭菌苗2毫升,以后每5~6个月免疫注射一次。大肠杆菌病。仔兔20日龄开始注射大肠杆菌多价菌,每次皮下注射1升,待仔兔断奶后再免疫一次,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月免疫一次。
Rabbit plague. At 40-45 days of age, young rabbits are subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of rabbit plague propolis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Pasteurella dual vaccine. At 60 days of age, they will receive another booster immunization, and then every 6 months thereafter. If this disease spreads, double the dose of vaccination is required in the epidemic area. Rabbit Pasteurella disease. After weaning, each piglet rabbit is injected with 1 milliliter of rabbit free Bacillus subtilis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Bacillus subtilis conjugate vaccine, and then injected every 4 months thereafter. Clostridium difficile disease. Weaned rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 2 milliliters of Clostridium difficile vaccine, and then immunized every 5-6 months thereafter. Escherichia coli disease. Starting from 20 days old, the piglets were injected with multivalent Escherichia coli bacteria subcutaneously at a dose of 1 liter each time. After weaning, the piglets were immunized again subcutaneously at a dose of 2 milliliters, and then immunized every 4 months thereafter.
波氏杆菌病。仔兔18日龄皮下注射波氏杆菌病菌苗1升,一周后强化免疫,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。
Bordetella infection. 18 day old rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of Bacillus subtilis vaccine. One week later, they were strengthened with 2 milliliters of the vaccine and injected every 4 months thereafter.
葡萄球菌病。在母免配种前皮下注射葡萄球菌病菌苗2毫升,保护期为4个月。
Staphylococcus disease. Subcutaneous injection of 2 milliliters of Staphylococcus aureus vaccine before maternal mating, with a protection period of 4 months.
五、价值及其他
5、 Value and Others
安哥拉兔适应性强。在我国北方也科饲养。产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。产毛量:公兔已达1720克,母免已达2036克。具有极高的经济价值。采毛时,一般从背部中线开始,由后向前推剪,依次为体侧、臀部、颈部、颌下、头部、腹部和四肢,也可以按照习惯进行。需要提醒的是,不能伤到长毛兔的皮肤,尤其是母兔的乳头,防止粗暴拔毛,万一失手伤到皮肤,应立即搽碘酒、止血。剪毛要一刀剪断,不剪二茬毛,以免降低兔毛等级。采毛时要边采毛边分级,将兔毛按级存放和保管。季节不同,采毛方法也不相同,夏季剪毛方式,剪毛尽量选择早、晚凉爽时进行,冬季采用拔毛方式,对于妊娠的母兔,还应留下腹毛。另外,采毛的器械还要注意,病兔剪毛必须单独进行,以防止皮肤病及其他传染病传播。
Angora rabbits have strong adaptability. It is also domesticated in northern China. High hair production, dense, slender, and soft coat, with a tuft structure arranged neatly and not easily tangled. The highest yield of wool: male rabbits have reached 1720 grams, and female rabbits have reached 2036 grams. Has extremely high economic value. When collecting hair, it is generally started from the midline of the back, pushed and cut from back to front, in order of the body side, buttocks, neck, submandibular area, head, abdomen, and limbs. It can also be done according to habits. It should be noted that the skin of long haired rabbits, especially the nipples of female rabbits, should not be injured to prevent rough plucking. In case of accidental skin injury, iodine solution should be immediately applied for disinfection and hemostasis. To cut the rabbit hair, one should cut it with one knife, not two strands, in order to avoid lowering the grade of the rabbit hair. When collecting fur, it is necessary to classify the raw edges and store and preserve the rabbit fur according to the grade. The methods of harvesting fur vary depending on the season. In summer, it is best to prune the fur, preferably in the cool early or late hours. In winter, it is best to pluck the fur. For pregnant female rabbits, abdominal fur should also be left behind. In addition, the equipment used for hair collection should also be disinfected, and the shearing of diseased rabbits must be done separately to prevent the spread of skin diseases and other infectious diseases.
四、病害防治
4、 Disease prevention and control
1、坚持自繁自养,新购兔隔离观察为了防止传染病的侵入,是自繁自养,确需引种时,要从非疫区购买。购入后隔离饲养2周以上,确认无病后方可放入兔场饲养。
1. Adhere to self breeding and self raising, and isolate newly purchased rabbits for observation. In order to prevent the invasion of infectious diseases, it is best to self breed and self raise. If introduction is necessary, it should be purchased from non epidemic areas. After purchase, isolate and raise for more than 2 weeks, and confirm that there is no disease before putting it into the rabbit farm for breeding.
2、搞好卫生卫生是防病的重要一环,通过以减少和消灭环境中的病原体,切断传播途径。饲养人员要求在更衣、换鞋、洗手后进入兔舍,进入场区的大门口应设池。外来工具、物品要经后再使用,常用工具及时清洗和晒。免舍、兔笼要坚持每天清扫一次,每周带免一次。
2. Good hygiene and disinfection is an important part of disease prevention. Through disinfection, pathogens in the environment can be reduced and eliminated, and transmission routes can be cut off. Breeding personnel are required to enter the rabbit house after changing clothes, shoes, and washing hands, and a disinfection pool should be set up at the entrance of the field. Foreign tools and items should be disinfected before use, and commonly used tools should be cleaned, disinfected, and sun dried in a timely manner. Free sheds and rabbit cages should be cleaned once a day and disinfected once a week.
3、搞好免疫免疫是控制传染病发生的一种重要手段,免疫搞好了,疫病就能得到有效的控制。由于各地区、各免场的疫病流行情况不同,因此也就不可能有一个可供各地统一使用的免疫程序,这就需要各养免场在实践中总结经验,制定符合具体情况的免疫程序。下面是几种常见病的免疫方法:
3. Improving immunity is an important means of controlling the occurrence of infectious diseases. Once immunity is improved, the disease can be effectively controlled. Due to the different epidemic situations in various regions and immunization sites, it is impossible to have a unified immunization program that can be used in different areas. This requires each immunization site to summarize their experience in practice and develop the best immunization program that is suitable for specific situations. Here are several common immunization methods for diseases:
兔瘟。仔兔40~45日龄皮下注射兔瘟蜂胶疫苗1笔升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,在60日龄时再加强免疫接种一次,以后每6个月免疫注射一次。若本病发生流行,在流行地区需加倍剂量免接种。兔巴氏杆菌病。仔兔断奶后每只注射兔离巴氏杆菌苗1毫升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。魏氏梭菌病。断奶仔兔皮下注射魏氏梭菌苗2毫升,以后每5~6个月免疫注射一次。大肠杆菌病。仔兔20日龄开始注射大肠杆菌多价菌,每次皮下注射1升,待仔兔断奶后再免疫一次,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月免疫一次。
Rabbit plague. At 40-45 days of age, young rabbits are subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of rabbit plague propolis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Pasteurella dual vaccine. At 60 days of age, they will receive another booster immunization, and then every 6 months thereafter. If this disease spreads, double the dose of vaccination is required in the epidemic area. Rabbit Pasteurella disease. After weaning, each piglet rabbit is injected with 1 milliliter of rabbit free Bacillus subtilis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Bacillus subtilis conjugate vaccine, and then injected every 4 months thereafter. Clostridium difficile disease. Weaned rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 2 milliliters of Clostridium difficile vaccine, and then immunized every 5-6 months thereafter. Escherichia coli disease. Starting from 20 days old, the piglets were injected with multivalent Escherichia coli bacteria subcutaneously at a dose of 1 liter each time. After weaning, the piglets were immunized again subcutaneously at a dose of 2 milliliters, and then immunized every 4 months thereafter.
波氏杆菌病。仔兔18日龄皮下注射波氏杆菌病菌苗1升,一周后强化免疫,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。
Bordetella infection. 18 day old rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of Bacillus subtilis vaccine. One week later, they were strengthened with 2 milliliters of the vaccine and injected every 4 months thereafter.
葡萄球菌病。在母免配种前皮下注射葡萄球菌病菌苗2毫升,保护期为4个月。
Staphylococcus disease. Subcutaneous injection of 2 milliliters of Staphylococcus aureus vaccine before maternal mating, with a protection period of 4 months.
五、价值及其他
5、 Value and Others
安哥拉兔适应性强。在我国北方也科饲养。产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。产毛量:公兔已达1720克,母免已达2036克。具有极高的经济价值。
Angora rabbits have strong adaptability. It is also domesticated in northern China. High hair production, dense, slender, and soft coat, with a tuft structure arranged neatly and not easily tangled. The highest yield of wool: male rabbits have reached 1720 grams, and female rabbits have reached 2036 grams. Has extremely high economic value.
本文由 长毛兔 友情奉献.更多有关的知识请点击 http://www.myxinhua.com/ 真诚的态度.为您提供为的服务.更多有关的知识我们将会陆续向大家奉献.敬请期待.长毛兔原译安哥拉兔,起源于小亚细亚一带,名字来自安哥拉城,即土耳其首都安卡拉。安哥拉兔从1723年由英国海员带到法国,再传到世界。后来形成了法、英、德和中四个不同的品系,长毛兔有白、黑、粟、蓝、灰、黄等多种颜色,白色兔的眼为红色,有色兔的眼睛为黑色。长毛兔白色兔毛有利染色,故饲养白色长毛免为普遍。
This article is a friendly contribution from Long haired Rabbit For more related knowledge, please click http://www.myxinhua.com/ Sincere attitude To provide you with comprehensive services We will gradually contribute more relevant knowledge to everyone Coming soon. Angora rabbit, originally translated from Angora rabbit, originated in Asia Minor, and its name comes from Angola City, namely Ankara, the capital of Türkiye. The Angora rabbit was brought to France by British sailors in 1723 and then spread to the world. Later, four different strains were formed, namely French, English, German, and Chinese. Long haired rabbits come in various colors such as white, black, millet, blue, gray, and yellow. White rabbits have red eyes, while colored rabbits have black eyes. Long haired rabbits have white rabbit fur that is conducive to dyeing, so raising white long haired rabbits is the most common.
详细介绍 PROFILE+
Detailed Introduction to PROFILE+
常见种类
Common types
德系
German
产于德国,是目前世界上饲养普遍、产毛量的品系。我国自1978年开始引进饲养。外貌特征。全身披厚密绒毛,被毛有毛丛结构,不易缠结,有明显波浪形弯曲。面部绒毛不甚一致,有的无长毛,也有额毛、颊毛丰盛的,但大部分耳背均无长毛,仅耳尖有。耳长中等、直立,头型偏宽而短。四肢强壮,肢势端正,胸部和背部发育良好。主要优缺点。德系安哥拉兔的主要优点是产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。主要缺点是繁殖性能较低,配种比较困难,初产母兔母性较差,且适应性较差。
Produced in Germany, it is currently the most commonly raised and highest yielding strain in the world. China has been introducing animal husbandry since 1978. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with thick and dense fur, with a tuft structure that is not easily tangled and has obvious wavy bends. The facial hair is not very consistent, some without long hair, while others have abundant hair on the forehead and cheeks. However, most of the earlobes do not have long hair, only the tips of the ears. The ears are of medium length and upright, with a broad and short head shape. Strong limbs, upright posture, well-developed chest and back. Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of German Angora rabbits are high hair production, dense, slender, and soft fur, with a tuft structure, neatly arranged, and not easily tangled. The main disadvantages are low reproductive performance, difficulty in mating, poor maternal quality of primiparous female rabbits, and poor adaptability.
法系
French legal system
产于法国,选育历史较长,是目前世界上的粗毛型长毛兔。我国早在20世纪20年代就开始引进饲养,1980年以来先后引进了.些新法系安哥拉兔。外貌特征。全身披白色长毛,粗毛含量较高。额部、颊部及四肢下部均为短毛,耳宽长而较厚,耳尖无长毛或有!撮短毛,耳背密生短毛,俗称“光板”。被毛密度差,毛质较粗硬,头型稍尖。新法系安哥拉兔体型较大,体质健壮,面部稍长,耳长而薄,脚毛较少。胸部和背部发育良好,四肢强壮,肢势端正。主要优缺点,法系安哥拉兔的主要优点是产毛量较高,兔毛较粗,粗毛含量高,适于纺线和作粗纺原料。适应性较强,耐粗性较好,繁殖力较高。主要缺点是被毛密度较差,面颊及四肢下部无长毛。该免适合以拔毛方式采毛,不宜剪毛。
Produced in France with a long history of breeding, it is currently the world's famous coarse haired long haired rabbit. China began introducing animal husbandry as early as the 1920s and has introduced it since 1980 Some New French Angora rabbits. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white long hair, with a high content of coarse hair. The forehead, cheeks, and lower limbs are all short haired, the ears are wide, long, and thick, and the tips of the ears have no or no long hair! Cuff short hair, densely covered with short hair on the back of the ear, commonly known as "Guangban". Poor hair density, coarse and hard hair texture, slightly pointed head shape. The New French Angora rabbit has a larger body size, robust physique, slightly longer face, long and thin ears, and less foot hair. The chest and back are well-developed, the limbs are strong, and the body posture is upright. The main advantages and disadvantages of French Angora rabbits are high wool production, thicker rabbit hair, high content of coarse hair, and suitability for spinning threads and as raw materials for coarse spinning. Strong adaptability, good tolerance to roughness, and high reproductive capacity. The main disadvantage is that the hair density is poor, and there is no long hair on the cheeks and lower limbs. This method is suitable for plucking hair and should not be pruned.
8系
8 series
产于日本,生产性能不及德、法系安哥拉兔。我国自1979年引进饲养,分布在江浙及辽宁等省。外貌特征。全身披白色浓密长毛,粗毛含量较少,不易缠结。额部、颊部、双耳外侧及耳尖部均有长毛,额毛有明显分界线。耳长中等、直立,头型偏宽而短。四肢强壮,肢势端正,胸部和背部发育良好。主要优缺点。日系安哥拉兔的主要优点是适应性强,耐粗性好,繁殖力强,母性好,泌乳性能高。仔兔成活率高,生长发育正常。主要缺点是体型较小,产毛量较低,兔毛品质一般,且个体间差异较大。
Produced in Japan, its production performance is inferior to that of Angora rabbits from Germany and France. Since 1979, China has introduced animal husbandry and it is distributed in provinces such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Liaoning. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with thick white fur, with a low content of coarse hair, which is not easily tangled. There are long hairs on the forehead, cheeks, outer sides of both ears, and tips of the ears, with clear dividing lines on the forehead hair. The ears are of medium length and upright, with a broad and short head shape. Strong limbs, upright posture, well-developed chest and back. Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of Japanese Angora rabbits are strong adaptability, good tolerance to roughness, strong reproductive ability, good maternal function, and high lactation performance. The survival rate of young rabbits is high, and their growth and development are normal. The main disadvantages are small body size, low hair production, average quality of rabbit hair, and significant individual differences.
英系
English series
产于英国,偏向于观赏和细毛型。我国早在20世纪20~30年代就开始引进饲养。外貌特征。全身披白色、蓬松、丝状绒毛,毛质细软。头型偏圆,额毛、颊毛丰满,耳短厚,耳尖密生绒毛,形似缨穗,有的整个耳背均有长毛,飘出耳外。四肢及趾问脚毛丰盛,背毛自然分开,向两侧披下。主要优缺点。英系安哥拉兔的优点是繁殖力强,被毛白色、蓬松,可作观赏用。缺点是被毛密度差,产毛量低,体质较弱,抗病力差,且母兔泌乳力较差。
Produced in the UK, it tends to be ornamental and fine haired. China began to introduce animal husbandry as early as the 1920s and 1930s. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white, fluffy, filamentous fur, with fine and soft texture. The head shape is slightly round, with full frontal and cheek hair, short and thick ears, densely covered with fluff at the tips of the ears, resembling tassels. Some have long hair on the entire back of the ears, floating out of the ears. The limbs, toes, and feet have abundant hair, and the back hair naturally separates and falls down to both sides. Main advantages and disadvantages. The advantage of the English Angora rabbit is its strong reproductive ability, white and fluffy fur, which can be used for ornamental purposes. The disadvantages are poor hair density, low hair production, weak constitution, poor disease resistance, and poor lactation ability of female rabbits.
>丹麦系
>Danish series
原产于丹麦,1980年引入我国。外貌特征。全身披白色、蓬松、柔软绒毛,头呈圆形或稍长型,皮肤紧密、细致,被毛丰满、浓密,多为短毛。有的耳尖长有!撮长毛,俗称“1撮毛”。主要优缺点。丹麦系安哥拉兔的主要优点是绒毛不易结块,产毛量较高主要特点是繁殖性能较差,与德系安哥拉兔繁殖性能相似。
Originating from Denmark, it was introduced to China in 1980. Appearance features. The whole body is covered with white, fluffy, and soft fur, the head is round or slightly long, the skin is tight and delicate, and the coat is full and dense, mostly short hair. Some ears have long tips! Cuo Mao, commonly known as "1 Cuo Mao". Main advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages of Danish Angora rabbits are that their fur is not easily clumped and their hair production is high. Their main feature is poor reproductive performance, which is similar to that of German Angora rabbits.
中系
Chinese-style
主要饲养于上海、江苏、浙江等地,系引进法系和英系安哥拉兔互相杂交,并导人白兔血液,经长期选育而成,1959年正式通过鉴走,命名为中系安哥拉兔。
Mainly raised in Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang and other places, the Angora rabbit is introduced from the French and English lineages and crossbred with each other, and introduced into the blood of Chinese white rabbits. After long-term breeding, it was officially named the Chinese Angora rabbit in 1959.
外貌特征。中系兔的主要特征是全耳毛,狮子头,老虎爪。耳长中等,整个耳背和耳尖均密生细长绒毛,飘出耳外,俗称“全耳毛”。头宽而短,额毛、颊毛异常丰盛,从侧面看,往往看不到眼睛,从正面看,也只是绒球团。脚毛丰盛,趾间及脚底均密生绒毛。骨骼细致,皮肤稍厚,体型清秀。
Appearance features. The main characteristics of Chinese rabbits are full ear hair, lion head, and tiger claws. The ear length is medium, and the entire back and tip of the ear are densely covered with slender hairs that float out of the ear, commonly known as "whole ear hair". The head is wide and short, with exceptionally abundant hair on the forehead and cheeks. When viewed from the side, the eyes are often not visible, and when viewed from the front, they are only fluffy balls. The foot hair is abundant, with dense fuzz between the toes and on the soles of the feet. The bones are delicate, the skin is slightly thick, and the body shape is delicate.
主要优缺点,中系兔的主要优点是性成熟早,繁殖力强,母性好,仔兔成活率高适应性强,较耐粗饲。体毛洁白,细长柔软形似雪球,可兼作观赏用。主要缺点是体型小,生长慢。产毛量低,被毛纤细,结块率较高,一般可达15%左右,公兔尤高。
The main advantages and disadvantages of Chinese rabbits are early sexual maturity, strong reproductive ability, good maternal function, high survival rate of offspring, strong adaptability, and tolerance to coarse feeding. The body hair is pure white, slender and soft, resembling a snowball, and can also be used for ornamental purposes. The main disadvantages are small body size and slow growth. Low hair production, fine coat, high clumping rate, generally up to 15%, especially for male rabbits.
形态及特征
Form and characteristics
毛发很浓密且是竖起的,但却不会像其它安哥拉免般常常掉毛,而质地亦较为坚韧。德系兔属细毛型,被毛密度大,每平方厘米达16000-18000根。有毛丛结构,不易缠结,产毛量高,年产毛量公兔为1190克,母兔为1406克,者达1700-2000克,毛长5.5-5.9厘米,年整殖3-4胎,每胎产仔6-7只,配种受胎率为53 6%本地安哥拉兔是我国在英系、法系安哥拉兔杂交的基础上掺入我国本地兔的血统并经长期选育而形成,其脚如虎爪,脚毛丰盛,背毛腹毛齐全。本地安哥拉免体型较小,骨骼较细,成年体重2.5~3.0千克。成年雄性兔体重达4.5千克,雌兔达4.9千克。公兔年产毛量为1千克以上,母兔1.2千克以上,毛质量好,不易结块,特一级毛的比例占总产毛量的75%以上。母兔初配年龄200日龄,年产4.5窝,胎产活仔7.2只。
The hair is thick and erect, but it does not shed hair as frequently as other Angolans, and the texture is also relatively tough. German rabbits belong to the fine haired type, with a high hair density of 16000-18000 hairs per square centimeter. The Angora rabbit has a tuft structure, is not easily tangled, and has a high hair production. The annual hair production of male rabbits is 1190 grams, and that of female rabbits is 1406 grams, with the highest reaching 1700-2000 grams. The hair length is 5.5-5.9 centimeters, and there are 3-4 litters per year, with 6-7 offspring per litter. The breeding and conception rate is 53.6%. The Angora rabbit is a hybrid of English and French Angora rabbits in China, with the addition of local rabbit bloodlines and long-term breeding. Its feet are like tiger claws, with abundant foot hair and complete dorsal and ventral hair. Local Angolans have a smaller body size and thinner bones, with an adult weight of 2.5-3.0 kilograms. Adult male rabbits weigh 4.5 kilograms, while female rabbits weigh up to 4.9 kilograms. The annual hair production of male rabbits is over 1 kilogram, and that of female rabbits is over 1.2 kilograms. The hair quality is good and not easy to clump. The proportion of special grade hair accounts for more than 75% of the total hair production. The first mating age of the female rabbit is 200 days old, with an annual production of 4.5 litters and 7.2 live offspring.
我孥锋的推届演1銫?讴巔弥郑年底餓始稭觴灶引进德系安哥拉兔,刚引进时,对我国的环境适应性较差,抗病力差,体型外貌不一致,遗传性不稳定,对饲养管理条件要求高。经过多年的适应和培育,该兔的成年兔体重平均4.23千克,比原种提高10.92%,平均年产毛量781克左右,一次剪毛量比原种提高11.27%。
I, Ying Feng, introduced the German Angora rabbit to our country at the end of the year. When it was first introduced, it had poor adaptability to the environment, poor disease resistance, inconsistent body shape and appearance, genetic instability, and high requirements for feeding and management conditions. After years of adaptation and cultivation, the average weight of adult rabbits in this rabbit is 4.23 kilograms, which is 10.92% higher than the original breed. The average annual hair production is about 781 grams, and the amount of hair cut per time is 11.27% higher than the original breed.
饲养方法
Feeding method
三观察
Three observations
一观察兔的精神状态,如发现免精神不振,眼睛无神,眼角湿润,耳色过红或过青,背毛蓬乱,卧伏不起或打喷,呼吸急促,这是兔不健康的表现。二观察兔的食欲情况,不健康免食欲不振,吃得少或蹲在一旁拒食。三观察兔粪形状的变化。患肠胃病的兔,粪便一头尖;患便秘的兔,粪干硬,大小不一致。
When observing the mental state of a rabbit, if it is found to be lacking in energy, with lifeless eyes, moist corners of the eyes, ears that are too red or too green, messy back hair, inability to get up or spray, and rapid breathing, these are unhealthy manifestations of the rabbit. Observe the appetite of the rabbit, and if it is unhealthy, it may lead to loss of appetite, eating less or squatting on the side to refuse to eat. Observe the changes in the shape of rabbit feces. Rabbits suffering from gastrointestinal diseases have a pointed head of feces; Rabbits suffering from constipation have dry and hard feces of varying sizes.
五不喂
Five not feeding
是不喂露水草;二是不喂腐烂发霉的饲料;三是不喂带泥、带沙土的饲料;四是不喂异味的草;五是有些饲料在某些生长阶段
Not feeding dew water plants; Secondly, do not feed on rotten or moldy feed; Thirdly, do not feed feed with mud or sand; The fourth is not to feed with smelly grass; Number five, some feed is available at certain growth stages
不能喂,如荞麦开花时,亚麻在籽粒、冠茎成熟时有毒,土豆特别是未成熟的土豆不能喂。
Cannot be fed, such as when buckwheat blooms, flax is toxic when the seeds and stems mature, and potatoes, especially immature potatoes, cannot be fed.
》九注意
》Nine Attention
一要注意预防疾病。二要注意选好种兔。三要注意适时选配。四要注意种兔管理,公母免都不能喂得过肥过瘦。公兔在配种期料量应增加25%,适当喂些豆类及大麦芽等:适时增加母兔营养,催情保胎,避免死胎。五要注意仔兔管理。应搞好母兔的产仔哺乳、饲喂、断乳及分群管理(大小兔分开饲养,每放15只为宜)。六要注意饲料多样化。七要注意给有特殊情况的兔"吃偏饭"。在饲喂中对老、弱、病、残、孕兔、哺乳母兔、仔幼免都要适当照顾,每天喂食4-5次;对病免要单独饲养和,防止传染。八要注意笼舍的方向和大小。夏朝东,冬朝南,兔笼长度大于兔体长的3倍,高出免体1.5倍。九要注意防止兔受三怕:一怕惊吓,二怕潮湿,三怕曝晒。
One must pay attention to preventing diseases. Secondly, it is important to choose the right breed of rabbits. Pay attention to timely selection and matching. Attention should be paid to rabbit breeding management, and both males and females should not be fed too fat or too thin. During the mating period, male rabbits should increase their feed intake by 25% and be fed with appropriate amounts of beans and barley malt. Female rabbits should also be given timely nutrition to promote estrus and prevent stillbirth. Pay attention to the management of young rabbits. We should do a good job in the birth, feeding, weaning, and grouping management of female rabbits (separate feeding of large and small rabbits, with 15 rabbits per square meter). Pay attention to the diversification of feed. Pay attention to providing special meals for rabbits with special circumstances. During feeding, appropriate care should be taken for the elderly, weak, sick, disabled, pregnant rabbits, nursing mothers, and young rabbits, feeding them 4-5 times a day; Disease control should be raised and treated separately to prevent transmission. Pay attention to the direction and size of the cage. Summer faces east, winter faces south, and the length of the rabbit cage is greater than three times the length of the rabbit's body and 1.5 times higher than the free body. Nine precautions should be taken to prevent rabbits from being afraid of three things: first, being scared, second, being damp, and third, being exposed to sunlight.
科学采毛
Scientific hair harvesting
选择合适的采毛时间和采毛方法,不仅能提高兔毛的产量和质量,还有利于种兔的配种繁殖。另外,适当缩短长毛免采毛的间隔时间,还可以增加长毛兔的年产毛量。长毛兔的采毛方法主要有剪毛和拔毛2种,拔毛又分为拔光和拔长留短2类。不同种类的长毛兔,采用的拔毛方法也不一样,粗毛型兔宜采用手拔毛,绒毛型兔则以剪毛为好。采用剪毛方式来毛,速度快、省时间,对幼兔、母兔没有不良影响,采用拔长留短则可以提高优级毛数量,而采用拔光的方法既可以提高粗毛质量,还可以提高产毛总产量。
Choosing the appropriate hair harvesting time and method can not only improve the yield and quality of rabbit hair, but also facilitate the breeding and reproduction of breeding rabbits. In addition, appropriately shortening the interval between long haired rabbits without hair harvesting can also increase the annual hair production of long haired rabbits. There are two main methods for harvesting the fur of long haired rabbits: shearing and plucking, which can be further divided into two categories: plucking the fur completely and plucking the long and leaving the short. Different types of long haired rabbits use different methods of plucking their fur. Coarse haired rabbits should be plucked by hand, while hairy rabbits should be pruned. Using shearing method for hair production is fast, time-saving, and has no adverse effects on young and female rabbits. Pulling out the long and leaving the short can increase the quantity of high-quality hair, while using the method of pulling out the light can not only improve the quality of coarse hair, but also increase the total yield of hair production.
采毛时,一般从背部中线开始,由后向前推剪,依次为体侧、臀部、颈部、颌下、头部、腹部和四肢,也可以按照习惯进行。需要提醒的是,不能伤到长毛兔的皮肤,尤其是母兔的乳头,防止粗暴拔毛,万一失手伤到皮肤,应立即搽碘酒、止血。剪毛要一刀剪断,不剪二茬毛,以免降低兔毛等级。采毛时要边采毛边分级,将兔毛按级存放和保管。季节不同,采毛方法也不相同,夏季剪毛方式,剪毛尽量选择早、晚凉爽时进行,冬季采用拔毛方式,对于妊娠的母兔,还应留下腹毛。另外,采毛的器械还要注意,病兔剪毛必须单独进行,以防止皮肤病及其他传染病传播。
When collecting hair, it is generally started from the midline of the back, pushed and cut from back to front, in order of the body side, buttocks, neck, submandibular area, head, abdomen, and limbs. It can also be done according to habits. It should be noted that the skin of long haired rabbits, especially the nipples of female rabbits, should not be injured to prevent rough plucking. In case of accidental skin injury, iodine solution should be immediately applied for disinfection and hemostasis. To cut the rabbit hair, one should cut it with one knife, not two strands, in order to avoid lowering the grade of the rabbit hair. When collecting fur, it is necessary to classify the raw edges and store and preserve the rabbit fur according to the grade. The methods of harvesting fur vary depending on the season. In summer, it is best to prune the fur, preferably in the cool early or late hours. In winter, it is best to pluck the fur. For pregnant female rabbits, abdominal fur should also be left behind. In addition, the equipment used for hair collection should also be disinfected, and the shearing of diseased rabbits must be done separately to prevent the spread of skin diseases and other infectious diseases.
四、病害防治
4、 Disease prevention and control
1、坚持自繁自养,新购兔隔离观察为了防止传染病的侵入,是自繁自养,确需引种时,要从非疫区购买。购入后隔离饲养2周以上,确认无病后方可放入兔场饲养。
1. Adhere to self breeding and self raising, and isolate newly purchased rabbits for observation. In order to prevent the invasion of infectious diseases, it is best to self breed and self raise. If introduction is necessary, it should be purchased from non epidemic areas. After purchase, isolate and raise for more than 2 weeks, and confirm that there is no disease before putting it into the rabbit farm for breeding.
2、搞好卫生卫生是防病的重要一环,通过以减少和消灭环境中的病原体,切断传播途径。饲养人员要求在更衣、换鞋、洗手后进入兔舍,进入场区的大门口应设池。外来工具、物品要经后再使用,常用工具及时清洗和晒。免舍、兔笼要坚持每天清扫一次,每周带免一次。
2. Good hygiene and disinfection is an important part of disease prevention. Through disinfection, pathogens in the environment can be reduced and eliminated, and transmission routes can be cut off. Breeding personnel are required to enter the rabbit house after changing clothes, shoes, and washing hands, and a disinfection pool should be set up at the entrance of the field. Foreign tools and items should be disinfected before use, and commonly used tools should be cleaned, disinfected, and sun dried in a timely manner. Free sheds and rabbit cages should be cleaned once a day and disinfected once a week.
3、搞好免疫免疫是控制传染病发生的一种重要手段,免疫搞好了,疫病就能得到有效的控制。由于各地区、各免场的疫病流行情况不同,因此也就不可能有一个可供各地统一使用的免疫程序,这就需要各养免场在实践中总结经验,制定符合具体情况的免疫程序。下面是几种常见病的免疫方法:
3. Improving immunity is an important means of controlling the occurrence of infectious diseases. Once immunity is improved, the disease can be effectively controlled. Due to the different epidemic situations in various regions and immunization sites, it is impossible to have a unified immunization program that can be used in different areas. This requires each immunization site to summarize their experience in practice and develop the best immunization program that is suitable for specific situations. Here are several common immunization methods for diseases:
兔瘟。仔兔40~45日龄皮下注射兔瘟蜂胶疫苗1笔升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,在60日龄时再加强免疫接种一次,以后每6个月免疫注射一次。若本病发生流行,在流行地区需加倍剂量免接种。兔巴氏杆菌病。仔兔断奶后每只注射兔离巴氏杆菌苗1毫升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。魏氏梭菌病。断奶仔兔皮下注射魏氏梭菌苗2毫升,以后每5~6个月免疫注射一次。大肠杆菌病。仔兔20日龄开始注射大肠杆菌多价菌,每次皮下注射1升,待仔兔断奶后再免疫一次,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月免疫一次。
Rabbit plague. At 40-45 days of age, young rabbits are subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of rabbit plague propolis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Pasteurella dual vaccine. At 60 days of age, they will receive another booster immunization, and then every 6 months thereafter. If this disease spreads, double the dose of vaccination is required in the epidemic area. Rabbit Pasteurella disease. After weaning, each piglet rabbit is injected with 1 milliliter of rabbit free Bacillus subtilis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Bacillus subtilis conjugate vaccine, and then injected every 4 months thereafter. Clostridium difficile disease. Weaned rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 2 milliliters of Clostridium difficile vaccine, and then immunized every 5-6 months thereafter. Escherichia coli disease. Starting from 20 days old, the piglets were injected with multivalent Escherichia coli bacteria subcutaneously at a dose of 1 liter each time. After weaning, the piglets were immunized again subcutaneously at a dose of 2 milliliters, and then immunized every 4 months thereafter.
波氏杆菌病。仔兔18日龄皮下注射波氏杆菌病菌苗1升,一周后强化免疫,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。
Bordetella infection. 18 day old rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of Bacillus subtilis vaccine. One week later, they were strengthened with 2 milliliters of the vaccine and injected every 4 months thereafter.
葡萄球菌病。在母免配种前皮下注射葡萄球菌病菌苗2毫升,保护期为4个月。
Staphylococcus disease. Subcutaneous injection of 2 milliliters of Staphylococcus aureus vaccine before maternal mating, with a protection period of 4 months.
五、价值及其他
5、 Value and Others
安哥拉兔适应性强。在我国北方也科饲养。产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。产毛量:公兔已达1720克,母免已达2036克。具有极高的经济价值。采毛时,一般从背部中线开始,由后向前推剪,依次为体侧、臀部、颈部、颌下、头部、腹部和四肢,也可以按照习惯进行。需要提醒的是,不能伤到长毛兔的皮肤,尤其是母兔的乳头,防止粗暴拔毛,万一失手伤到皮肤,应立即搽碘酒、止血。剪毛要一刀剪断,不剪二茬毛,以免降低兔毛等级。采毛时要边采毛边分级,将兔毛按级存放和保管。季节不同,采毛方法也不相同,夏季剪毛方式,剪毛尽量选择早、晚凉爽时进行,冬季采用拔毛方式,对于妊娠的母兔,还应留下腹毛。另外,采毛的器械还要注意,病兔剪毛必须单独进行,以防止皮肤病及其他传染病传播。
Angora rabbits have strong adaptability. It is also domesticated in northern China. High hair production, dense, slender, and soft coat, with a tuft structure arranged neatly and not easily tangled. The highest yield of wool: male rabbits have reached 1720 grams, and female rabbits have reached 2036 grams. Has extremely high economic value. When collecting hair, it is generally started from the midline of the back, pushed and cut from back to front, in order of the body side, buttocks, neck, submandibular area, head, abdomen, and limbs. It can also be done according to habits. It should be noted that the skin of long haired rabbits, especially the nipples of female rabbits, should not be injured to prevent rough plucking. In case of accidental skin injury, iodine solution should be immediately applied for disinfection and hemostasis. To cut the rabbit hair, one should cut it with one knife, not two strands, in order to avoid lowering the grade of the rabbit hair. When collecting fur, it is necessary to classify the raw edges and store and preserve the rabbit fur according to the grade. The methods of harvesting fur vary depending on the season. In summer, it is best to prune the fur, preferably in the cool early or late hours. In winter, it is best to pluck the fur. For pregnant female rabbits, abdominal fur should also be left behind. In addition, the equipment used for hair collection should also be disinfected, and the shearing of diseased rabbits must be done separately to prevent the spread of skin diseases and other infectious diseases.
四、病害防治
4、 Disease prevention and control
1、坚持自繁自养,新购兔隔离观察为了防止传染病的侵入,是自繁自养,确需引种时,要从非疫区购买。购入后隔离饲养2周以上,确认无病后方可放入兔场饲养。
1. Adhere to self breeding and self raising, and isolate newly purchased rabbits for observation. In order to prevent the invasion of infectious diseases, it is best to self breed and self raise. If introduction is necessary, it should be purchased from non epidemic areas. After purchase, isolate and raise for more than 2 weeks, and confirm that there is no disease before putting it into the rabbit farm for breeding.
2、搞好卫生卫生是防病的重要一环,通过以减少和消灭环境中的病原体,切断传播途径。饲养人员要求在更衣、换鞋、洗手后进入兔舍,进入场区的大门口应设池。外来工具、物品要经后再使用,常用工具及时清洗和晒。免舍、兔笼要坚持每天清扫一次,每周带免一次。
2. Good hygiene and disinfection is an important part of disease prevention. Through disinfection, pathogens in the environment can be reduced and eliminated, and transmission routes can be cut off. Breeding personnel are required to enter the rabbit house after changing clothes, shoes, and washing hands, and a disinfection pool should be set up at the entrance of the field. Foreign tools and items should be disinfected before use, and commonly used tools should be cleaned, disinfected, and sun dried in a timely manner. Free sheds and rabbit cages should be cleaned once a day and disinfected once a week.
3、搞好免疫免疫是控制传染病发生的一种重要手段,免疫搞好了,疫病就能得到有效的控制。由于各地区、各免场的疫病流行情况不同,因此也就不可能有一个可供各地统一使用的免疫程序,这就需要各养免场在实践中总结经验,制定符合具体情况的免疫程序。下面是几种常见病的免疫方法:
3. Improving immunity is an important means of controlling the occurrence of infectious diseases. Once immunity is improved, the disease can be effectively controlled. Due to the different epidemic situations in various regions and immunization sites, it is impossible to have a unified immunization program that can be used in different areas. This requires each immunization site to summarize their experience in practice and develop the best immunization program that is suitable for specific situations. Here are several common immunization methods for diseases:
兔瘟。仔兔40~45日龄皮下注射兔瘟蜂胶疫苗1笔升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,在60日龄时再加强免疫接种一次,以后每6个月免疫注射一次。若本病发生流行,在流行地区需加倍剂量免接种。兔巴氏杆菌病。仔兔断奶后每只注射兔离巴氏杆菌苗1毫升或兔瘟-巴氏杆菌二联苗2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。魏氏梭菌病。断奶仔兔皮下注射魏氏梭菌苗2毫升,以后每5~6个月免疫注射一次。大肠杆菌病。仔兔20日龄开始注射大肠杆菌多价菌,每次皮下注射1升,待仔兔断奶后再免疫一次,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月免疫一次。
Rabbit plague. At 40-45 days of age, young rabbits are subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of rabbit plague propolis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Pasteurella dual vaccine. At 60 days of age, they will receive another booster immunization, and then every 6 months thereafter. If this disease spreads, double the dose of vaccination is required in the epidemic area. Rabbit Pasteurella disease. After weaning, each piglet rabbit is injected with 1 milliliter of rabbit free Bacillus subtilis vaccine or 2 milliliters of rabbit plague Bacillus subtilis conjugate vaccine, and then injected every 4 months thereafter. Clostridium difficile disease. Weaned rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 2 milliliters of Clostridium difficile vaccine, and then immunized every 5-6 months thereafter. Escherichia coli disease. Starting from 20 days old, the piglets were injected with multivalent Escherichia coli bacteria subcutaneously at a dose of 1 liter each time. After weaning, the piglets were immunized again subcutaneously at a dose of 2 milliliters, and then immunized every 4 months thereafter.
波氏杆菌病。仔兔18日龄皮下注射波氏杆菌病菌苗1升,一周后强化免疫,皮下注射2毫升,以后每4个月注射一次。
Bordetella infection. 18 day old rabbits were subcutaneously injected with 1 liter of Bacillus subtilis vaccine. One week later, they were strengthened with 2 milliliters of the vaccine and injected every 4 months thereafter.
葡萄球菌病。在母免配种前皮下注射葡萄球菌病菌苗2毫升,保护期为4个月。
Staphylococcus disease. Subcutaneous injection of 2 milliliters of Staphylococcus aureus vaccine before maternal mating, with a protection period of 4 months.
五、价值及其他
5、 Value and Others
安哥拉兔适应性强。在我国北方也科饲养。产毛量高,被毛密度大、细长、柔软,有毛丛结构,排列整齐,不易缠结。产毛量:公兔已达1720克,母免已达2036克。具有极高的经济价值。
Angora rabbits have strong adaptability. It is also domesticated in northern China. High hair production, dense, slender, and soft coat, with a tuft structure arranged neatly and not easily tangled. The highest yield of wool: male rabbits have reached 1720 grams, and female rabbits have reached 2036 grams. Has extremely high economic value.
本文由 长毛兔 友情奉献.更多有关的知识请点击 http://www.myxinhua.com/ 真诚的态度.为您提供为的服务.更多有关的知识我们将会陆续向大家奉献.敬请期待.
This article is a friendly contribution from Long haired Rabbit For more related knowledge, please click http://www.myxinhua.com/ Sincere attitude To provide you with comprehensive services We will gradually contribute more relevant knowledge to everyone Coming soon.